In today’s dynamic business landscape, understanding what is staffing can make or break an organization’s success. For German companies, where precision and efficiency are cultural cornerstones, staffing is more than just filling vacant positions—it’s about strategically aligning talent with organizational goals. Whether you’re a small startup in Berlin or a multinational in Munich, the process of staffing shapes your workforce, drives productivity, and fosters growth. This blog dives into the intricacies of staffing, exploring its definition, processes, and significance, tailored specifically for German businesses aiming to thrive in a competitive market. Let’s embark on a journey to uncover how effective staffing can transform your organization.
Defining Staffing for German Businesses
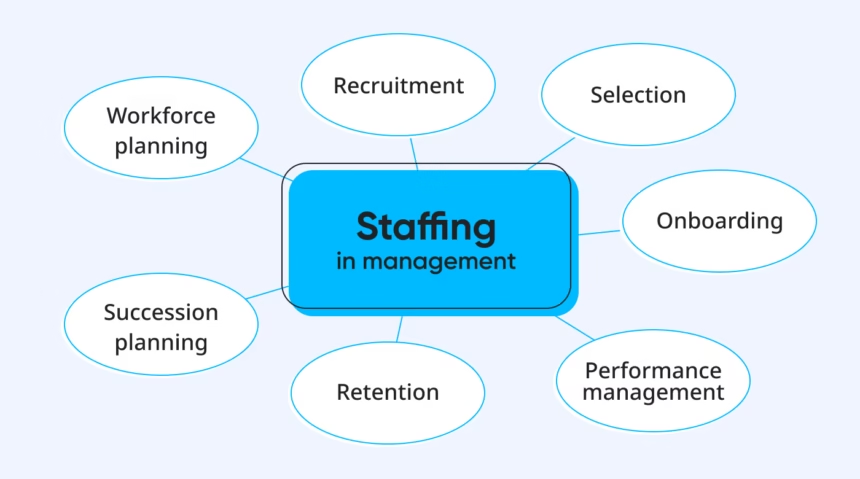
Staffing, at its core, is the process of identifying, recruiting, selecting, and retaining employees to meet an organization’s needs. However, for German corporations, this method is deeply intertwined with the country’s established labor market and high standards for workforce quality. Staffing isn’t just about hiring; it involves forecasting staff wishes, ensuring compliance with German labor laws, and building a group that displays the agency’s values. According to Dr. Sabine Mueller, a human resource management expert, “Effective staffing is the spine of organizational success, particularly in Germany, wherein a skilled workforce is a competitive gain” (Mueller, 2019, Journal of Business Research).
Moreover, staffing encompasses both short-term and long-term strategies. For instance, a tech company in Hamburg might need temporary developers for a task, while a manufacturing plant in Bavaria may focus on permanent hires for operational stability. Therefore, staffing requires a balance of pliability and foresight, ensuring that the right expertise is in place at the proper time.
The Staffing Process Explained
The staffing process is a multi-faceted adventure that demands meticulous planning. It starts with workforce planning, where organizations investigate current and future staffing needs based on goals and marketplace trends. In Germany, where industries like automotive and engineering dominate, this step is crucial to staying ahead of talent shortages. For instance, a company anticipating growth in electric car manufacturing must proactively recruit engineers with specialized knowledge.
Recruitment and Selection
Next, recruitment takes center level. This includes sourcing candidates through task boards, social media, or expert networks like Xing, which is famous in Germany. However, German agencies must also navigate cultural expectations, including valuing formal qualifications and structured interviews. Once applicants are sourced, selection follows, wherein employers evaluate abilities, cultural health, and alignment with organizational goals.
Onboarding and Retention
Finally, onboarding and retention ensure that new hires combine seamlessly and continue to be engaged. In Germany, where employee loyalty is prized, supplying competitive advantages and clean career paths is crucial. Thus, the staffing procedure is a continuous cycle of planning, hiring, and nurturing talent.
Importance of Staffing in Germany
Effective staffing is a game-changer for German organizations, particularly in a marketplace recognized for its excessive requirements and worldwide competitiveness. Firstly, staffing without delay impacts productivity. A properly-staffed crew, prepared with the proper abilities, drives innovation and performance—key drivers of fulfillment in industries like production and era. Conversely, poor staffing decisions can result in expensive turnover and neglected possibilities.
Ensuring Legal Compliance
Additionally, staffing ensures compliance with Germany’s stringent labor regulations. From adhering to the Works Constitution Act to respecting collective bargaining agreements, organizations must align their staffing strategies with legal frameworks. This is mainly applicable for small and medium-sized firms (SMEs), which form the spine of Germany’s economic system. For these corporations, staffing errors may have disproportionate monetary and operational impacts.
Promoting Diversity
Furthermore, staffing displays an agency’s commitment to range and inclusion. In Germany, where immigration is reshaping the workforce, companies that embrace numerous skills pools gain a competitive side. By prioritizing inclusive staffing, groups not only beautify creativity but also appeal to a broader client base.
Challenges in Staffing for German Companies
Despite its significance, staffing is not without demanding situations, mainly in Germany’s precise labor marketplace. One tremendous hurdle is the lack of professional employees, mainly in STEM fields. According to a 2021 study in German Economic Review, Germany faces a growing hole in technical information, with industries like IT and engineering suffering to find certified candidates (Schmidt & Weber, 2021).
Cultural Expectations
Another challenge is navigating cultural expectations. German employees often prioritize job security and work-life balance, which can complicate recruitment for roles requiring flexibility or relocation. Additionally, the bureaucratic nature of German labor laws can slow down the hiring process, especially for international candidates requiring visas.
Adapting to Remote Work
Finally, the rise of remote work has added complexity to staffing. While remote opportunities attract global talent, they also require businesses to rethink traditional office-based models. For German companies accustomed to structured workplaces, adapting to hybrid staffing models is both a challenge and an opportunity.
Strategies for Effective Staffing
To overcome these challenges, German businesses can adopt several strategies to enhance their staffing efforts. Firstly, leveraging technology is crucial. Applicant tracking systems (ATS) and AI-driven recruitment tools can streamline candidate sourcing and evaluation, saving time and resources. Platforms like StepStone and LinkedIn are particularly effective for reaching German professionals.
Building Employer Branding
Secondly, investing in employer branding is essential. A strong employer brand, showcasing a company’s culture and values, attracts top talent in a competitive market. For instance, offering flexible work arrangements or professional development opportunities can set a company apart. In Germany, where employees value stability, highlighting long-term career prospects is particularly effective.
Collaborating with Education
Moreover, collaborating with educational institutions can address skill shortages. Partnerships with universities or vocational schools, such as Germany’s renowned dual education system, allow businesses to train future employees early. This approach is especially valuable in industries like manufacturing, where hands-on experience is critical.
Prioritizing Retention
Finally, prioritizing employee retention is as important as recruitment. Regular feedback, competitive salaries, and a supportive work environment foster loyalty. By focusing on retention, businesses reduce turnover costs and build a committed workforce.
Staffing and German Business Culture
Germany’s business culture, rooted in precision and reliability, shapes its approach to staffing. For instance, German employers often prioritize formal qualifications and certifications, reflecting the country’s emphasis on education. This cultural trait influences hiring decisions, with candidates’ academic backgrounds carrying significant weight.
Team-Oriented Workplaces
Additionally, Germany’s collectivist work environment values teamwork and collaboration. Staffing strategies must therefore focus on building cohesive teams rather than just individual talent. This is evident in the popularity of team-based assessments during recruitment, where cultural fit is as important as technical skills.
Union Influence
Furthermore, Germany’s strong union presence impacts staffing. Collective bargaining agreements often dictate wages, working hours, and benefits, requiring businesses to align their staffing policies with union expectations. Understanding these cultural nuances is critical for effective staffing in Germany.
The Future of Staffing in Germany
Looking ahead, staffing in Germany is poised for transformation, driven by technological advancements and demographic shifts. Automation and AI are reshaping recruitment, enabling faster and more accurate candidate matching. However, these tools must be used ethically to avoid bias and ensure fairness.
Demographic Shifts
Demographically, Germany’s aging population is creating both challenges and opportunities. As older workers retire, businesses must attract younger talent and upskill existing employees. Additionally, immigration is diversifying the workforce, requiring inclusive staffing practices to integrate international talent effectively.
Sustainability in Staffing
Sustainability is another emerging factor. German consumers and employees increasingly value environmentally responsible companies, and staffing strategies must reflect this. For example, businesses that prioritize green initiatives in their employer branding are likely to attract eco-conscious talent.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what is staffing is essential for German businesses aiming to thrive in a competitive and regulated market. From workforce planning to retention, staffing is a strategic process that shapes organizational success. By addressing challenges like skill shortages and cultural expectations, and adopting strategies like technology integration and employer branding, companies can build a workforce that drives growth and innovation. As Germany’s business landscape evolves, staffing will remain a cornerstone of success, requiring adaptability and foresight. For German businesses, mastering staffing is not just a task—it’s an opportunity to create a vibrant, future-ready organization.